Computer Science & IT
Coding & Algorithms Development
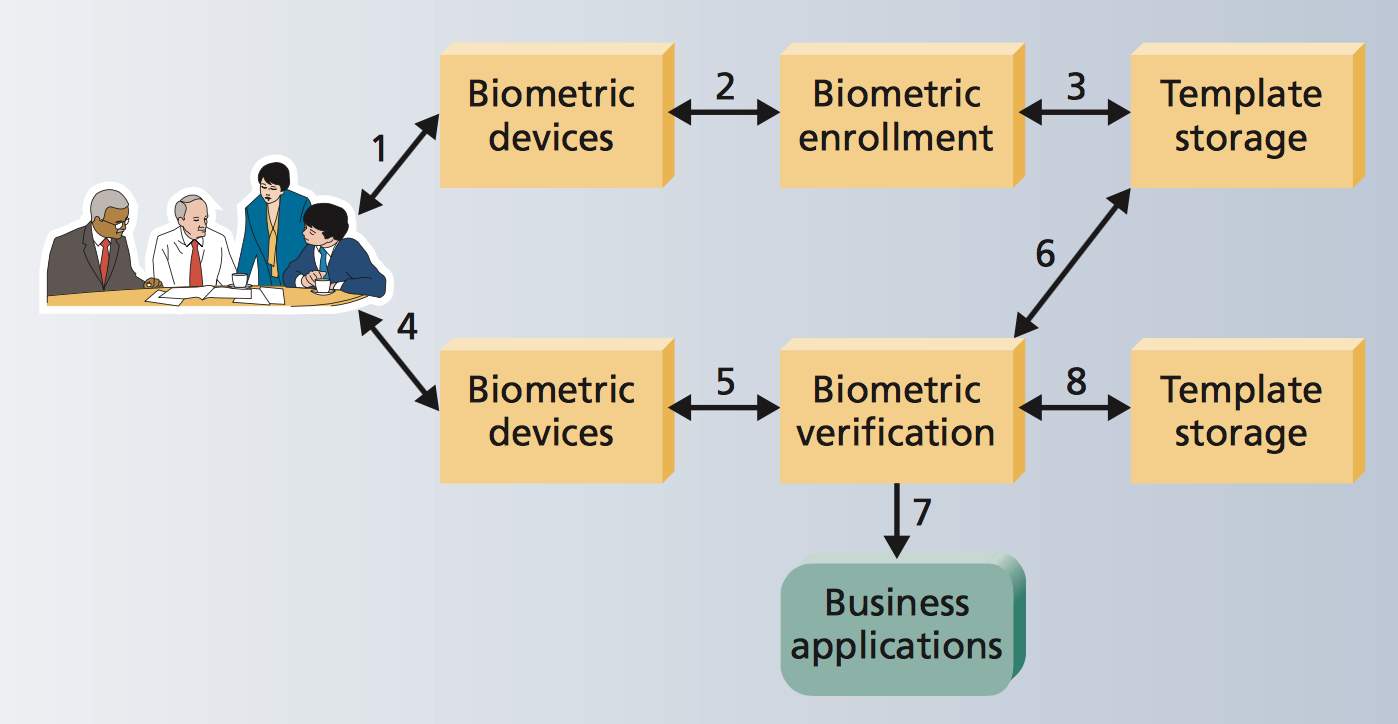
Literature Review on Security Issues in Biometric Authentication
Biometric identification refers to the process of comparing a digital picture of a bodily component to a previously saved image in the system. The advantage of utilising biometrics to validate the authorised user over passwords is because biometrics include fingerprints, facial recognition, speech patterns, and retina scans. User authentication is the most important component of any information system’s security. People are urged to utilise this technology to increase network security, however this poses a difficulty at this moment. Biometrics are not secret, but they may be duplicated, faked, and recorded by fakers.
The statistical study and measurement of a person’s unique physical and behavioural traits is known as biometrics. For many years, people have been judged by their physical characteristics such as their face, movement, and voice. In the mid-nineteenth century, Alphonse Bertillon, the head of the police department’s criminal distinguishing proof section, devised and refined body estimates to identify criminals.
In government ventures, Biometrics examines. The government is using the concept of biometrics in the Aadhar card to connect the general public, which is incredibly beneficial in assembling the data of every native that can be used for advanced financial and social planning. Another advancement in biometrics is Soft Biometrics, a relatively new concept in biometrics that includes the estimate of statistical highlights from the biometric structure. The assessment of sexual orientation, age, origin, hair-, eye-, and skin-shade, as well as other natural data from body parts such as fingerprints, face, and palm prints, is unmistakably delicate biometrics.