Medical & Healthcare
Research Methodology
Qualitative Research on Applied Phenomenology
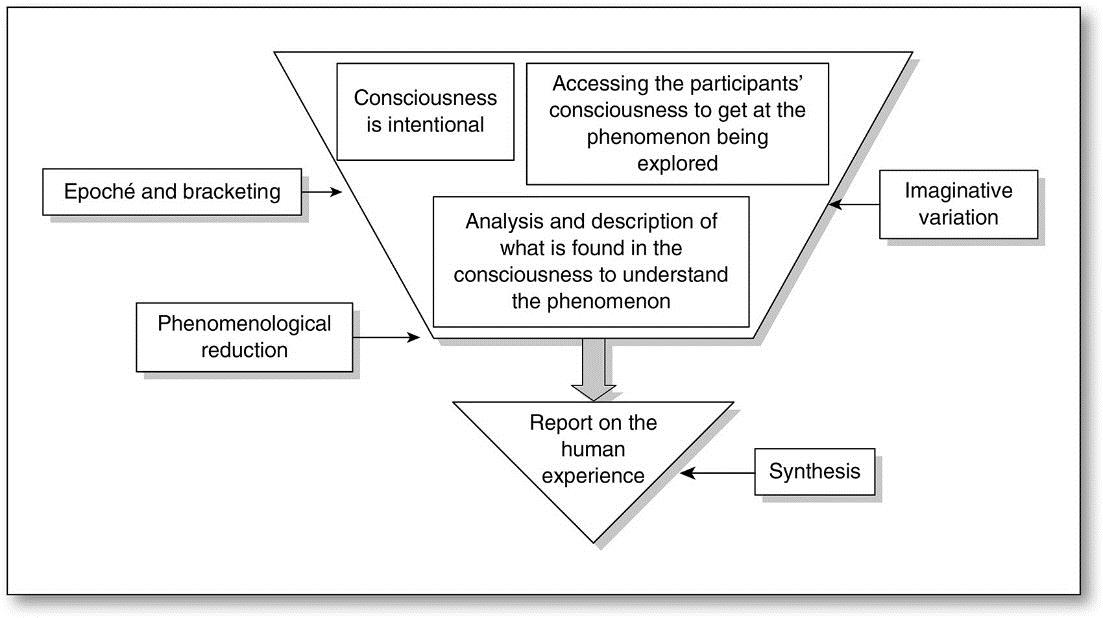
The phenomenological approach seeks to highlight the specific by identifying events as they are seen by the participants in a scenario. Phenomenology is concerned with the study of experience from the individual’s perspective, “bracketing” commonly held beliefs and perceptual patterns.
Phenomenological methods emphasise the significance of personal perspective and interpretation and are founded on a paradigm of personal knowledge and subjectivity. As a result, they’re useful for deciphering subjective experience, obtaining insights into people’s motives, and cutting through the clutter of assumed assumptions and common knowledge.
Other basically qualitative techniques, such as ethnography, hermeneutics, and symbolic interactionism, have overlaps with phenomenological research. Pure phenomenological research aims to describe rather than explain, and it does it without the use of assumptions or preconceived notions.
Phenomenological approaches are particularly successful at bringing to the fore individual experiences and perceptions from their own points of view, and therefore challenging structural or normative assumptions. Adding an interpretative component to phenomenological research allows it to educate, support, or question policy and action by allowing it to be utilised as the foundation for practical theory.
Phenomenological methods are effective at bringing up difficult problems and allowing people to speak out. This isn’t always easy for clients or funders, especially when the study contradicts widely held beliefs or threatens the existing quo. Many organisations, on the other hand, value the insights that a phenomenological approach may provide in terms of cutting through presumptions, spurring action, or confronting complacency.