Management and regulation risk
In Brief
- Global Financial crisis has contributed to heightened significanceof regulatory risk management
- Enforcement risk is an entity’s inability to comply with laws and regulations, procedures, policies, legislation and standards
- Effective policies for internal risk management are to ensure that people are aware of the demands and follow guidance.
- Companies should be recommended to collaborate with third-party organizations, implement IT in especially data analytics, and control the product life cycle Framework in order to conform to external mandates.

Introduction
Regulatory risks are key worry nowadays for company owners. After the Financial crisis, the federal government and other regulatory authorities have increasingly involved in the creation and implementation of policies for corporate.
Global financial crisis led to an increased importance of regulatory risk management
Although credit and market risk have long been on the radar of higher Management, recent regulatory changes focusing on enhanced capital adequacy, liquidity, accountability and customer safety put greater importance on successful Mechanisms for risk Management.
The financial crisis highlighted significant weaknesses in bank and risk control approaches. A result is the shifting emphasis of the competitiveness of the company and more by consumer requirements. Financial resilience is the latest slogan and by improved structures and directives, loopholes found in regulation and management are being filled (Ozdemir, 2020).
Firms offering financial services are under growing strain to handle regulatory enforcement and related damages more efficiently. Risk management and avoidance at both business and operation level, details of record storing and difficulty maintaining them deserve far more consideration.
Practice demonstrates that the accuracy and credibility of the data should not be taken lightly and it may be expensive to get it wrong. The expense of inadequate enforcement is generally both financial and reputational, as per the demonstrations of recent high penalties levied mainly by US regulators on key financial houses.
With current Basel III capital adequacy and liquidity system on the path for adoption over the next few years, and changing requirements imposed by Western national policymakers and regulators, the risk of property collecting and using the correct data for risk management has become crucial (Sharma, 2020).
While UAE banks were relatively untouched by this worldwide bank crisis, the slump in the real-estate sector in 2009 highlighted that local banks need to provide clearer data on exposures relevant to industries so that institutions can better withstand shocks and banks can provide sufficient and reliable services under different circumstances.
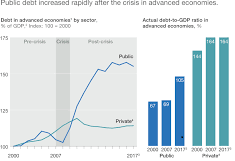
Figure 1: (mckinsey, 2020)
What is compliance risk actually?
There are four specific risk types – financial, operational, regulatory and strategic – all mitigated by internal controls. Compliance vulnerability is the failure of an entity to conform to laws and regulations, protocols, practices, legislation and mandates. Some sectors are more controlled and they pose a higher probability of regulatory enforcement (Hu, 2020). Both businesses pose regulatory enforcement threats, which ensures their own corporate rules and practices are not met. The secret to mitigating such threats is to implement controls routinely that ensure that the company satisfies its internal and external specifications.

Figure 2: (eltoma-global, 2020)
What are some of the best practices for internal enforcement risk management?
You ought to provide clear and well-reported processes and practices. Constant preparation from top to bottom is then necessary. Make sure everyone knows his or her demands from a process and policy perspective.
At the backend, you need to check – cyclic check-ins on specific events to ensure that people are upholding the guidelines and looking for patterns (Gorgo et al., 2019). Are their patterns and behaviors that display scarcity of conformity? If it does, question the reason behind it. Do you need any more Guidance for people? Do people violate the laws, legislations, policies, and processes and if they disobey, what is the actual motive? Alternatively, is there a flaw in the handling of the mechanism?
How to suggest companies to obey what is externally mandated?
There is a common awareness of whether there are such laws in effect – defending people, respecting certain companies. However, a number of companies are falling because of lack of funds or adequate expertise to conduct the enforcement Research necessary to handle such level of risk. We are grappling with issues like costs and profits and how long to support them. Most corporate owners realize the expense of running a business; and are working on it and look for opportunities to do so successfully. Others consider drastic actions like going against political leaders in an effort to make the standards, rules, and legislations less effective.
One successful approach of handling this challenge is taking advantage of established third-party organizations. You should get temporary staff to help work around the regulatory criteria, using a varied cost rather than a fixed cost Framework.
Information Technology, especially data analytics has a huge role to play in spotting the risk areas for the practices of management and regulations (Wijethilake & Lama, 2019). This is an area where technology can come handy in driving efficacy. Regulatory tools can dig out data from the systems, run consecutive tests on it, and let you know if something is not compliant to the law, policy, or procedures.
Figure 3: (raconteur, 2020)
Today’s problem is becoming even more intense. There is an enormous growth for data and all that remains unorganized. Besides, regulatory and litigation based continuity standards are aggravating the issues. It is obvious that the future market gains from improved Data Control and Management. With more efficient data preservation and quality control techniques, businesses will gain enhanced risk reduction and decreased data storing expenses, as well as largely expanded regulatory enforcement.
An effective benefit of the data life cycle management system will allow companies to control expenses, maintain the correct records, and meet regulatory criteria for enforcement. Equally significant, by offering a sound forum for decision-making, it will raise the market benefit of the results. Therefore, do not be scared of using the cost-effectiveness of technology.
Likewise, do not be insinuated by your view of the expense as if you do not deal with the risk and adopt the outside resources and technology, what would be the effect if risk actually comes? Disregarding risk is a serious mistake.
You need to recognize your risks and then try to handle the risk proactively and purposefully by internal controls (Younas & Kassim, 2019). Yet, this is something, which many small organizations avoid but they should not, as they are not in a position to bear the burden if anything big goes wrong.
Conclusion
Finally, we can say that regulatory risk Management relies on the importance of the inside data of the records generated, its interpretation and assessment. Where data accuracy is insufficient, a good base for handling risk and compliance is missing. Top management and boards should pay attention to these factors.
Reference
- Gorgo, M., Raczkowski, K. & Kraft, F. (2019). Compliance Risk Management in Polish and German Companies. Journal of Intercultural Management. [Online]. 11 (4). p.pp. 115–145. Available from: https://content.sciendo.com/view/journals/joim/11/4/article-p115.xml.
- Hu, Y. (2020). Research on the Construction of Ecosystem in Compliance Risk Management of Foreign Trade Enterprises in Fujian Province. In: 5th International Conference on Economics, Management, Law and Education (EMLE 2019). [Online]. 2020, Atlantis Press, pp. 483–486. Available from: https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/emle-19/125931471.
- Ozdemir, L. (2020). Volatility Spillover Between Stock Prices and Trading Volume: Evidence From the Pre-, In-, and Post Global Financial Crisis Periods. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics. [Online]. 5. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fams.2019.00065/full.
- Sharma, S. (2020). Basel Norms in Indian Banking Industry and its Current Status: A Review Based Study. Studies in Indian Place Names. [Online]. 40 (50). p.pp. 3126–3148. Available from: https://archives.tpnsindia.org/index.php/sipn/article/view/4353.
- Wijethilake, C. & Lama, T. (2019). Sustainability core values and sustainability risk management: Moderating effects of top management commitment and stakeholder pressure. Business Strategy and the Environment. [Online]. 28 (1). p.pp. 143–154. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/bse.2245.
- Younas, M.A. & Kassim, A.A.M. (2019). Essentiality of internal control in Audit process. [Online]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Aza_Azlina_Md_Kassim/publication/337655414_Essentiality_of_internal_control_in_Audit_process/links/5def0c8aa6fdcc2837147841/Essentiality-of-internal-control-in-Audit-process.pdf.
- How secure is the global financial system a decade after the crisis? (2020). [Online] Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/how-secure-is-the-global-financial-system-a-decade-after-the-crisis (Accessed: 13 April 2020).
- Services, E. (2020) Compliance Risk Management Services, Eltoma-global.com. [Online] Available at: http://eltoma-global.com/services/compliance-risk-management-services.html (Accessed: 13 April 2020).
- How data analytics is reshaping risk management – Raconteur (2020). [Online] Available at: https://www.raconteur.net/sponsored/how-data-analytics-is-reshaping-risk-management (Accessed: 13 April 2020).

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post