What is a Practical Gap in a Literature Review?
What is a literature review?
A literature review can be described as an organised method of collecting and synthesising previous research. An effective and well-conducted literature review establishes a solid foundation for increasing knowledge and aiding theory development. A literature review can help answer a research question by integrating findings and viewpoints from numerous empirical findings. A literature review must be well-structured, convey a study’s findings, and identify the gaps. Check out our literature review examples for guidance on the structure of a literature review.
A literature review is crucial since it helps to discover areas where more research is needed by providing an overview of the areas where research involves multiple disciplines and where it is inadequate, thereby helping the researcher get dissertation ideas. The inadequacy of the previous literature constitutes the literature gaps or research gaps (Snyder, 2019).
What is a research gap?
A research gap can be defined as an area or a topic where inadequate or missing information hinders a researcher’s ability to reach a conclusion for a research question. The gaps in the research may be used to conduct further research to answer the question (Sabbaghtorkan, 2020). Identifying a research gap is crucial since it adds value and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. Various types of research gaps have been identified, which are as follows-
- Evidence Gaps
- Knowledge Gaps
- Practical Gaps,
- Methodological Gaps,
- Empirical Gaps,
- Theoretical Gaps and
- Population Gaps (Miles, 2017)
Practical gaps are becoming increasingly important among the numerous forms of research gaps, as recognising them leads to the development of methods for the effective implementation of research findings.
A practical gap is a form of research gap that is concerned with translating research findings into practice. It refers to the discrepancy between research findings and their practical application in the real world. This gap is frequently observed when study findings are not applied as intended or are not implemented at all.
Suppose a study reveals that a specific teaching style is more effective in enhancing student performance, but teachers are not implementing it in their classrooms. In that scenario, there is a practical gap between the research findings and their application in practice. Likewise, there is a practical gap if a study reveals that a new medical treatment is more effective than the current treatment but is not commonly adopted in clinical practice.
Identifying practical gaps can aid researchers as well as practitioners in developing methods for putting research findings into practise. This could entail creating policies, instruction plans, or other materials to support evidence-based practices. Researchers may guarantee that their study has a significant impact on bettering outcomes for people, organisations, and communities by addressing practical gaps.
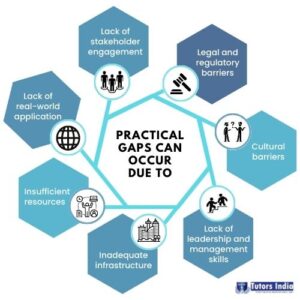
- Insufficient resources: When there are inadequate resources to put a suggested solution into practise, a practical gap may occur. For instance, a suggested intervention to lower child malnutrition may call for expensive equipment that is difficult to come by in a context with little resources.
- Inadequate infrastructure: When a proposed solution cannot be supported by the necessary infrastructure, a practical gap may result. For instance, a proposed waste management solution would need a proven recycling system, which might not exist in a certain area.
- Lack of real-world application: When theoretical ideas or models do not apply in the real world, a practical gap might develop. For instance, while a theoretical model for sustainable development might exist, it might not have been put into practice. This kind of practical gap could be addressed by proposing feasible solutions, like the growth of sustainable enterprise in Guinea.
- Lack of stakeholder engagement: When there is a lack of stakeholder involvement in the suggested solution, a practical gap can occur. For instance, if community people are not actively involved in the planning and implementation process, a proposed solution to improve community health may fail.
- Legal and regulatory barriers: When legal or regulatory obstacles prevent the implementation of a suggested solution, a practical gap may develop. For instance, laws that permit the use of specific fuels may make it difficult to implement a proposed solution to reduce air pollution.
- Cultural barriers: When cultural obstacles inhibit the use of a recommended solution, a practical gap can result. For instance, cultural norms that restrict women’s access to healthcare could make it difficult to implement a suggested strategy aimed at improving women’s health.
- Lack of leadership and management skills: A practical gap can occur whenever there is a lack of managerial and leadership skills required to put a proposed solution into action. A proposed remedy to improve the efficiency of a healthcare system, for example, may necessitate strong leadership and managerial skills, which may be missing in a particular setting.
Conclusion
A literature review involves systematically collecting and synthesising previous research, which helps the researcher find areas of inadequacy, known as research gaps. Research gaps can be classified as knowledge gaps, practical gaps, evidence gaps, methodological gaps, empirical gaps, theoretical gaps and population gaps. A practical gap occurs when there is a discrepancy between a research finding and the practical application of the finding. Practical gaps may occur due to a lack of practicability, insufficient resources, inadequate infrastructure, a lack of stakeholder engagement, legal regulatory and cultural barriers and a lack of leadership and management skills.
At Tutors India, we assist Masters students in writing a well-structured and correctly referenced literature review. Our team is diverse, with experts from various disciplines from recognised universities with experience in academic writing. We ensure the assistance offered is per the university guidelines. In addition, we also offer study materials and free samples that make the student more confident in writing literature reviews in the future.
References-
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, 333-339.
Sabbaghtorkan, M., Batta, R., & He, Q. (2020). Prepositioning of assets and supplies in disaster operations management: Review and research gap identification. European Journal of Operational Research, 284(1), 1-19.
Miles, D. (2017), A Taxonomy of Research Gaps: Identifying and Defining the Seven Research Gaps

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post