Economics & Finance
Assignment Writing
- Economic trends in key markets
- Consumption and Service sectors
- Supply chain resilience
- Economic Integration
- Macroeconomic aspects of nutrition policy
- Four Pillars of GDP
- Four factors affecting the business cycle
- Three broad areas of financial decision making
- Merger accounting
- Inventory Audit Or Leverage & Profitability Or FDI
- Profitability Vs FDI
- UK Banking Industry- A Competition Commission’s Banking Report
Economic Integration
Economic integration is defined both as a state of affairs and as a process. According to the process, economic integration contains the set of economic and political actions that has been designed to eradicate discrimination between economic units.
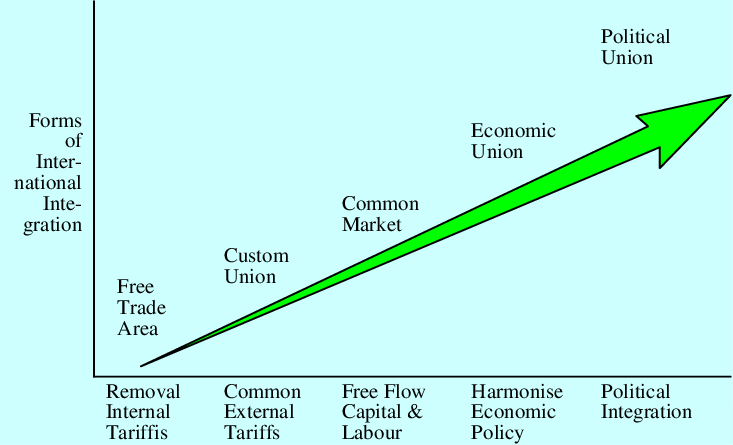
There are many types of economic integration.
- Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs): Arrangements in which member nations get tariff reductions or privileged treatment in quantitative limitations on their business with other member nations even as maintaining their business limitations against third parties.
- Free Trade Areas (FTAs): Member nations remove business barriers amongst themselves even as maintaining their individual state barriers against third parties.
- Customs Unions (CUs): This is an arrangement where member nations eradicate all barriers to do business amongst them and accept common tariffs to be applied to other countries.
- Common Markets (CMs): Arrangements that contain all the features that define custom unions, but also permit for full mobility of factors of manufacturing.
- Economic Unions (EUs): This is the most absolute form of economic integration. In addition to comprising the features of Common Markets, Economic Unions imply the absolute coordination of fiscal, monetary, industrial, and welfare policies, in addition to, the establishing a common prototype of foreign affairs.
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Forms-of-economic-integration_fig1_236171355
