Economics & Finance
Assignment Writing
- Economic trends in key markets
- Consumption and Service sectors
- Supply chain resilience
- Economic Integration
- Macroeconomic aspects of nutrition policy
- Four Pillars of GDP
- Four factors affecting the business cycle
- Three broad areas of financial decision making
- Merger accounting
- Inventory Audit Or Leverage & Profitability Or FDI
- Profitability Vs FDI
Macroeconomic Aspects of Nutrition Policy
Human being’s nutritional status has been influenced by their health and consumption of food. In turn, health is influenced by the accessibility of sanitation, health, and other related programs. Economic crises are often related to or caused by surplus spending by the government. Governments often try to slash the amount spent on social programs, such as for health care, as a part of the macroeconomic policies on nutrition. Macroeconomic policies are classified into five general types: monetary, exchange rate, fiscal, foreign trade, and price and wage.
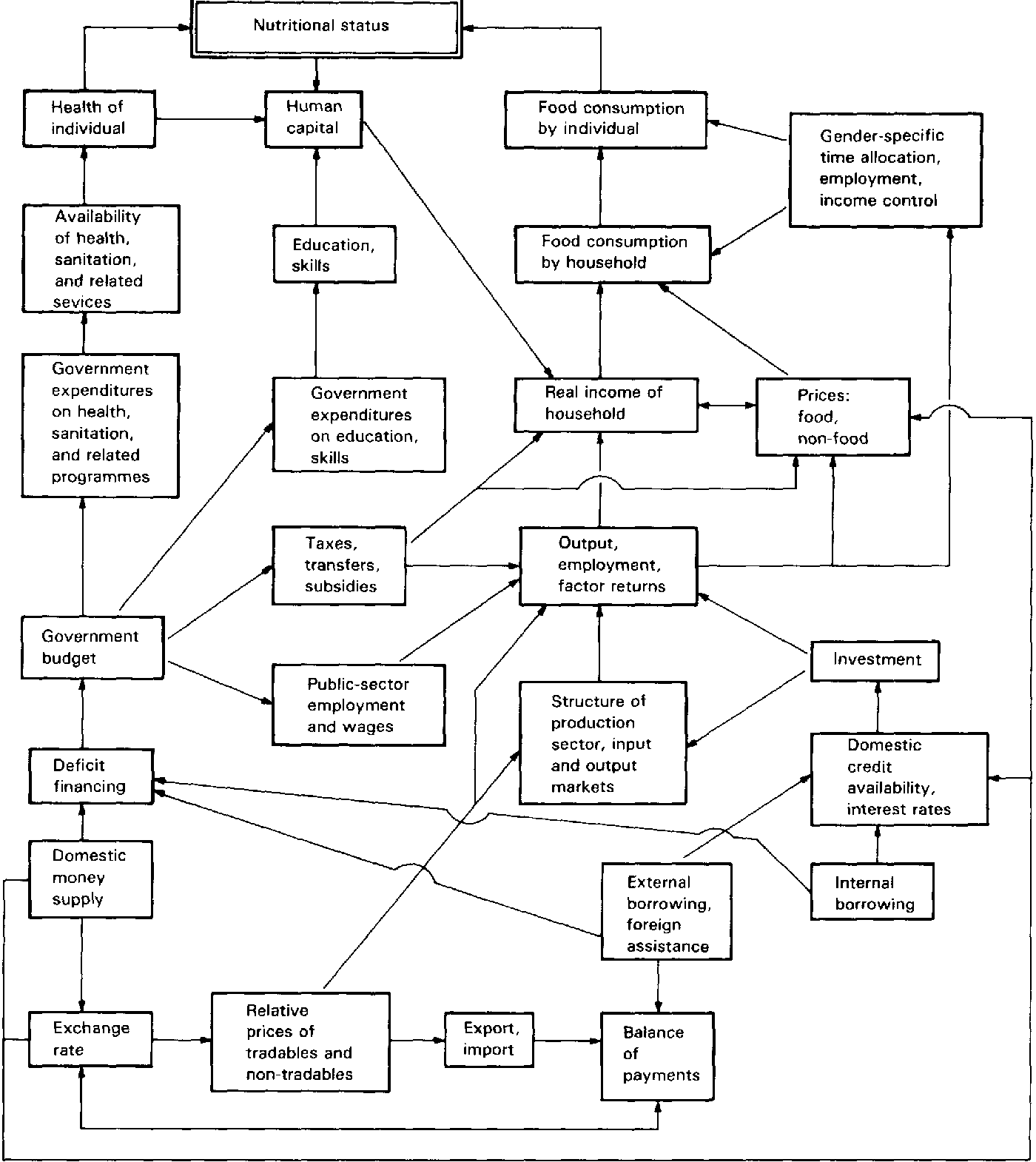
Source: http://www.nzdl.org/cgi-bin/library?e=d-00000-00—off-0ccgi–00-0—-0-10-0—0—0direct-10—4——-0-1l–11-en-50—20-about—00-0-1-00-0–4—-0-0-11-10-0utfZz-8-00&cl=CL1.6&d=HASH4b28eff70c72e401869ed5.2.8&gc=1
Monetary policies usually pay attention to restricting the increase in money supply and availability of domestic credit, and increase savings. Procedures are taken to control interest rates and limit credit for certain sectors.
Fiscal policies usually intend to restrict discrepancies in government spending via restraints on expenses and, less significantly, through extended revenues of the government. Actions to reduce expenses include limited explicit funding on food and other services and goods. It also intends to limit spending in social programs such as education, health care, and transfers of direct income. Efforts have been taken to limit discrepancies in public-sector enterprises. Limitations of employment in public sectors and limited wages are also often found in macroeconomic policies. Such policies also bring changes to employment opportunities and income for women.
