Engineering & Technology
Tips For Developing Secure And Flexible Management Policy For Multiple Users Over The Cloud
Sep 18, 2019RESEARCH REPORT
In Brief:
General background
With the ascent of Cloud Computing (CC), a huge number of clients and different applications have looked to speak with one another, swapping sensitive information (Werner, Westphall, & Westphall, 2017). In consequences, for efficiently managing various resources and applications, the use of tools and models is significant for securely managing different user identities as well as avoiding compromising data privacy. For this, most of them suggested a federated identity management process which utilizes the privacy appliances towards assisting in consistence with current legislation. In the section, we analyse the privacy and security issues in cloud identity management and relating the features and challenges. At the end we discuss brief note of recommendation for Developing Secure and Flexible Management Policy for both multiple Users and cloud system.
See also: Security and Privacy Issues over the Cloud EnvironmentSee also: Secure Access Control Framework for Fully Fledged Network Security Control
Significance and need of identity management and fine-grained access control policies
Generally, the CC improves the managing capability of computing sources through merging the concepts like on-demand use, elasticity and resource allocation in a dynamic manner (Eludiora et al., 2011). However, for multiple users, cloud system and huge amount of data in the field of big data application becomes complex (Subashini & Kavitha, 2011) wherein the concern of privacy issues. In this perspective, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is frequently used towards providing access control facilities and control identity of data. Few of the identity management (IM) tools utilizes with appropriate individualities (S. Singh, Jeong, & Park, 2016) by considering various mechanism for addressing privacy issues. But, till there is an issue like user data leakage, lack of control on the dissemination of personal information are recurring and distribution of unnecessary attributes in cloud environments (Castiglione et al., 2015; A. Singh & Chatterjee, 2015). So, to obtain cloud identity management as well as met the present regulation, the providers should protect the user privacy, data, entities and data throughout their lifecycle. (Indu, Anand, & Bhaskar, 2018; Werner et al., 2017). This identity management procedure will meet the requirement fine-grained access control process and user flexibility of data access.
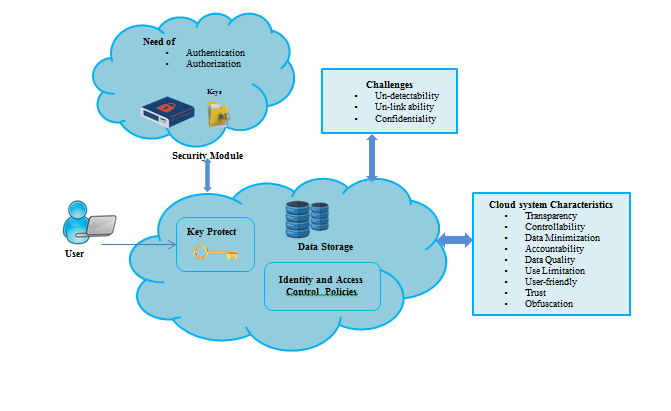
Figure 1: Overview of Cloud Storage System Based on Characteristics, Need and Challenges
IM components dealt with the need for authorization and authentication Legillon et al. (2013) in the cloud environment (Oliveira, Trinta, Vieira, & Cortes, 2018). The pictorial representation of Cloud Storage System with respect to the system Characteristics, Need and Challenges are discussed in figure 1.
Authentication (AN)
The term AN is defined as the process of approving an entity via other entity which is used to ensure whether the application or person is qualified for claiming or accessing data. The common AN approaches are third party authentication, 3D password objects, digital device authentication, multifactor authentication, simple text passwords, biometric authentication and graphical passwords. Nowadays, cloud access consent is granted via the IM system (Butun, Erol-Kantarci, Kantarci, & Song, 2016; Indu et al., 2018).
Authorization (AR)
Based on the authenticated user’s entitlements, the AR will be disagreeing or permitting access to a particular resource. AR decides like what applications or which user is permitted to make on system and application/user identity data are used for decision making (Khan et al., 2014). The cloud network comprises various service providers in which a single user can access various services at same time whereas each service from various security levels and service provider (Indu et al., 2018).
For ensuring the valid user’s access (for various services and resources) in IAM system, an access control governance cloud service provider (CSPs) defines the set of policies which is relevant to the access control. To meet the objective of each organization, CSPs should ensure the significant features such as Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) (Indu et al., 2018; Zhang, Zheng, Li, Li, & Li, 2016).
Identity & access management systems
First, the term IM is a process of managing, creating using identities and infrastructure which offered support for these processes. Also, it is capable of performing functions like discovery, policy enforcement, information exchange, administration, maintenance, management and data authentication. Each application or person identified through credential that denotes a group of attributes, delivered through reliable resources (Werner et al., 2017).
To ensure the security in IAM, the data’s are approved and managed by the same identity for entire applications. It is used to validate the data users, services or devices as well as have rights to access or deny data. Moreover, it does not need its own authentication or identity to authenticate the data (Indu et al., 2018). The IAM simplifies the management of large-scale distributed systems which minimizes the application workload.
Recommendation
From the above points, we concluded that there is a need for effective key-based authentication to enhance the performance of flexible management for both multiple users and cloud system.
Also required authorization policies for multi-party cloud infrastructure data sharing as it offers flexible and dynamic operations.
Summary
This section summarized and analysed the recent security, mitigations and potential threats aspects in cloud system along with the significance of data access management, identity management, services and security concern. From this we found there is a need for effective IAM mechanism for development of secure and flexible management policies which will enhance the system performance in both security and privacy concern.


